Dr. Chen Xiao talks about Hong Kong: Too many people have removed their teeth that could have been preserved
Dr. Chen Xiao is a very popular dentist in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and a senior dentist who has worked in the Vickong Dental Stomatology team for more than 15 years. In the early quarter of this year, Dr. Chen received many dental customers from Hong Kong. Compared with the situation of dental customers in Shenzhen, Dr. Chen said that the tooth loss of customers who come to medical treatment in Hong Kong is more serious! The main reasons include: periodontal inflammation and timely treatment, tooth decay to the remaining teeth, loss of tooth defects caused by trauma, and removal of teeth in the dental unit.

Some customers gave feedback that they went to consult for root canal treatment, hoping to keep the teeth, but they were told to pull out the teeth directly for dental implant. Doctors who are willing to do a good job in dental treatment are really rare!
Dr. Chen introduced, Du tooth root (also known as: root canal treatment) is mainly used for the professional treatment of dental pulp disease, periapical disease and other dental diseases. Treatment can control infection, promote the healing of periapical lesions or prevent the development of periapical lesions.
The root can be divided into two types according to the use of microscope and microscopic instruments, as follows:
1. Routine Du tooth root: this method is used in general patients. The advantage is that the operation is relatively simple, without the need to use a microscope.
2. Microscopic root: Microscopic root canal treatment is required when the disease involves the lateral branch root canal or the missing root canal. The advantages are the possible treatment of small lesions, while the disadvantages are that the operator is more demanding and the process is more complex.
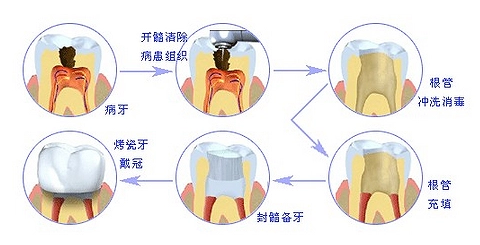
1. Indications for dental root:
If the patient is identified, the dentist will recommend dental root treatment:
1. Endopal diseases: various types of pulpitis, pulp necrosis, dental resorption and pulp calcification that cannot preserve living pulp.
2. Periapical disease: acute periapical inflammation must be treated with root canal after remission of acute symptoms, and all types of chronic periapical inflammation.
3. Combined periodontal-pulp lesions.
4. Trauma teeth: the root has been developed, the crown is broken, the pulp is exposed, or the broken crown is not exposed, but the restoration design needs full crown or pile core crown repair, or the broken root can be retained for repair.
5. Some non-carious dental hard tissue diseases, such as severe enamel hypoplasia, severe abrasion, tooth fissure, etc.
6. Affected teeth with intention to remove the pulp: other patients with normal pulp, such as maxillofacial surgery or denture repair.
2. contraindication:
1. It is not suitable for root canal therapy if the patient has:
2. Periodontal and (or) severe dental defects that cannot be preserved.
3. The affected teeth with no function or preservation significance in the dentition.
4, suffering from more serious systemic diseases, generally poor physical condition, unable to tolerate the treatment process.
5, limited mouth opening, unable to do Du tooth root diagnosis and treatment operation.
3. Appropriate timing of dental root: usually, if patients find toothache, apical gingival swelling and other symptoms during physical examination or specialist examination, indicating the existence of pulp disease or periapical disease, doctors will recommend timely root canal treatment.
4. Du root postoperative note: through root canal treatment, teeth should reduce or avoid chewing hard things, if conditions permit, suggest to do all porcelain crown or porcelain dental implant restoration, in order to better protect the teeth, reduce adverse reactions such as tooth fracture, let each natural tooth can be more long service to body health and improve happiness.



